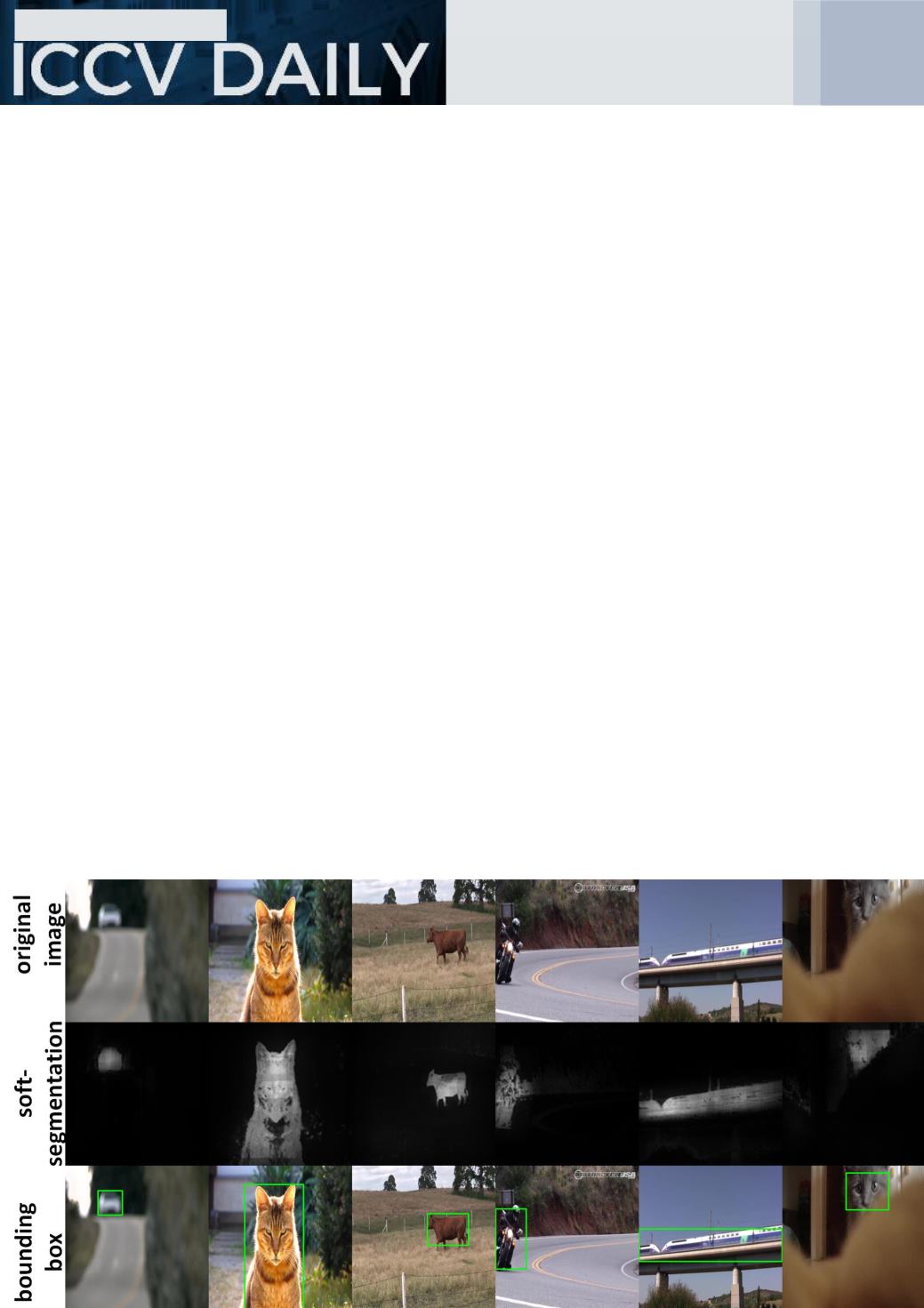
He then added, “
There is something
that nature tries to tell us in video. If
we just look at random pictures from
the internet, it’s very hard to discover
things in an unsupervised way.
Whereas in video, we have this
consistency over space and time. We
have co-currencies of certain patterns.
We can take advantage of them in
order to discover what might be
related to a certain object
.”
They took a very general approach that
could work well with deep learning as
well as with any type of classifier. In
supervised learning, most works go
towards the hard cases of positive and
negative examples. They came up with
a completely different idea and
decided to start with the easy cases
where they could select with high
precision, positive samples.
Marius explained, “
We can pretend
that they are positive samples, even
though the recall is low, which means
we don’t get all of them, but we get
some of them using certain cues. Then
we learn a classifier, and we also have
a theoretical result which proves that
this will be almost equivalent to having
the full set of positives. This classifier,
the next iteration, will increase the
recall while keeping the precision high.
This means that now, we have the
positives, and we can come up with a
better classifier. In this way, the next
iteration classifier is richer, stronger,
and so on
.”
15
Friday
“There is something that
nature tries to tell us in
video. If we just look at
random pictures from
the internet, it’s very
hard to discover things in
an unsupervised way.
Whereas in video, we
have this consistency
over space and time. ”
Marius and Ema