Orthopedic surgeries such as hip or knee replacement are performed via an incision which often compromises the surrounding tissue. The assimilation of RAS into these surgeries significantly decreases the incision size and allows sparing of more tissue compared with standard surgeries. In addition, RAS possess higher accuracy and precision during the procedure. The combination of smaller incision, less damage to nearby tissue, and better accuracy for implant placement, results in faster recovery, lower pain levels reported, and fewer complications.
Improve Procedural Planning with AI
The first step towards a tissue sparing approach in RAS is detailed and adequate planning. This usually involves careful examination of the anatomy using a CT scan, modelling of the anatomy to select an implant, and planning a path for the orthopedic surgery. All these steps can be improved using AI:
- Segmentation of bones and joints can be done accurately and efficiently using deep learning methods, resulting in an accurate 3D model of the anatomy without time consuming manual segmentation. This model allows user-friendly anatomical examination.
- Once a 3D model is available, it can be used to fit different implants, and assess which one complies best.
- This 3D model can be used to plan the procedure – find the best spot for the incision and learn directions and dimensions to reach the desired goal.
This segmentation solution is well established and can be tailored specifically for any use-case.
Improve Procedure using Accurate Measurements and 3D Perception
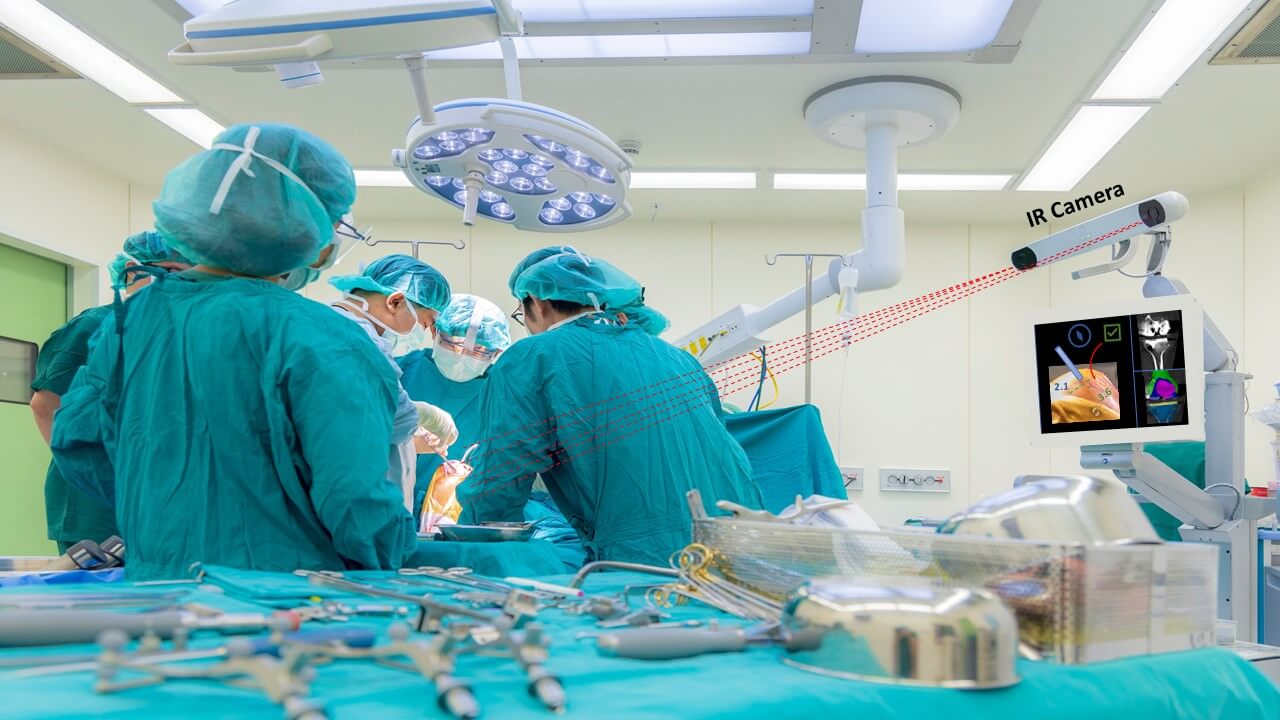
Sparing tissue in a procedure requires minimal incisions and careful tool handling. During the procedure it is important to continuously keep track of tool position relative to the anatomy while following the procedural plan. Any diversion will result in misplacement of the implant and deeper and wider incisions, ultimately increasing the risk for complications.
Using standard or depth cameras (after calibration), in combination with advanced deep learning algorithms, we can accurately track each tool and detect its position in relation to the body’s coordinate system and the OR’s coordinate system. Once the robotic arms and tools are well positioned and controlled, the procedural plan can be followed as designated, with minimal human error. The system can also issue warnings when needed.
When the surgeon is in control of the robotic hands, any viewing aid can assist to achieve better results. Simple tasks like drilling and stitching can be done with improved precision using 3D perception. The information received from depth or stereo cameras can be altered using computer vision algorithms into a topographic image of the anatomy and surgical tools, providing a 3D perspective for the surgeon.
Add AI to your Surgical Robot
Investing in more accurate orthopedic surgical robots will significantly reduce harm to surrounding tissue during procedures. AI and computer vision gives an added value in this aspect to any robot, with minimal hardware change. RSIP Vision’s experience and expertise in this field can add such modules to your device, enabling superior accuracy and adding value to the solution. Contact us today!

 Surgical
Surgical