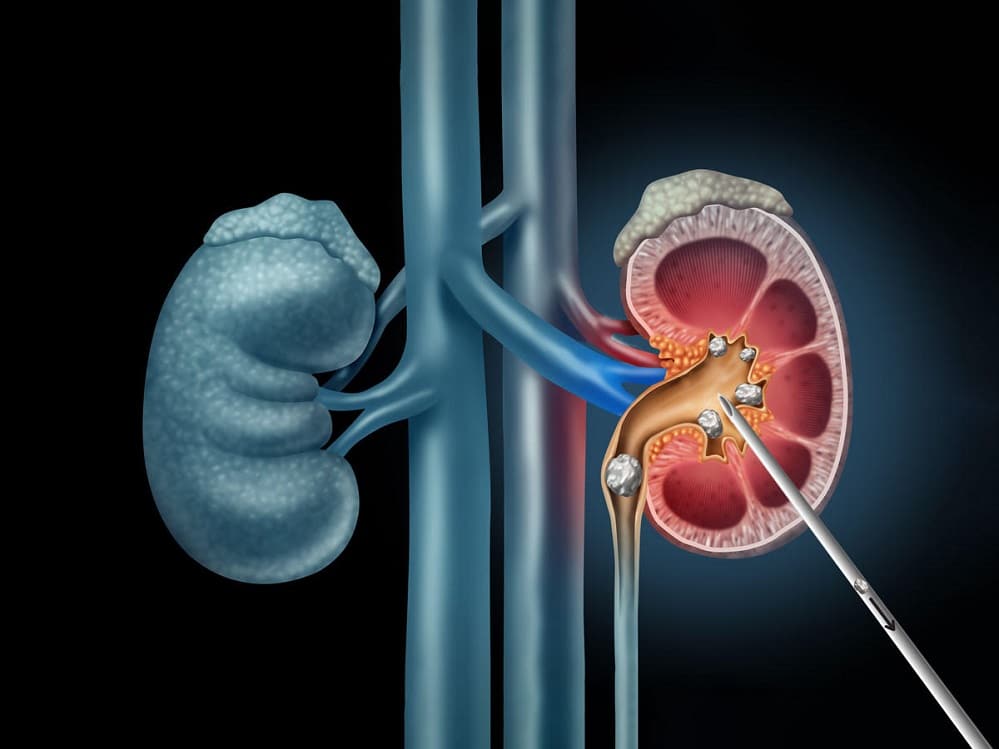
Urolithiasis, or kidney stones, is a common pathology affecting nearly 10% of the population in the USA. Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL) is a minimally invasive urology procedure intended to remove stones from the kidney and proximal ureter which are less amiable to other endourological modalities, specifically large stones, or in the presence of abnormal anatomy. This procedure requires real-time ultrasound and/or X-ray guidance and is usually preceded with a CT scan for diagnosis.
Gaining access is the first and most challenging part of the procedure. The tract needs to be created in the exact direction and depth of the kidney’s collecting system and in close proximity to the stone. This becomes more challenging in cases where multiple stones need to be targeted, and it is preferred to avoid the need for a second tract. Hence, obtaining a precise tract is essential for a successful and safe procedure.
To achieve the desired accuracy, the surgeon uses fluoroscopy, ultrasound, or both, to position the needle in the correct angle and to verify the needle’s depth. Both modalities suffer from inherent disadvantages: ultrasound has poor image quality and fluoroscopy does not allow depth estimation. Another issue is the radiation exposure with fluoroscopy. Excess radiation is harmful to the patient and the operating-room staff and hence minimizing it is desired.
RSIP Vision proposes a unique set of tools for planning and navigation during PCNL:
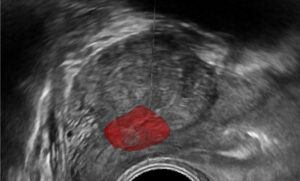
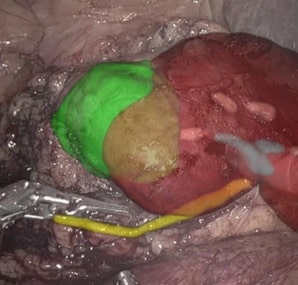
- Procedure Planning: The pre-op scan contains both high resolution and 3D information. RSIP Vision’s dedicated deep-learning (DL) algorithms can detect and segment the kidney stones, as well as surrounding anatomic structures. Using this output, a detailed surgical plan can be developed – from point of incision, to needle angle and depth penetration, and even further planning of specific methods for stone removal.
- Image Registration: A combination of advanced Artificial Intelligence and classic computer-vision algorithms are trained to accurately register the fluoroscopy and ultrasound images with the pre-op scan, overlaying the detailed planning map on the real-time images. This tool provides needle position and direction within the 3D information of the pre-op scan, adding a depth dimension in real-time.
- Needle Tracking: State-of-the-Art tracking modules follow the needle and provide an accurate estimation of the needle position within the images. This provides continuous assessment of the needle position and allows correction if needed.
Combining these tools provides the surgeon with real-time, precise information about the stone location and the needle position throughout the procedure, reducing risk of complications and speeding up the surgery. This set of tools can be introduced into robotic systems, thus improving PCNL outcomes even more by using Artificial Intelligence and the robot’s precision.
RSIP Vision has a proven track-record of implementation of segmentation, registration, and tracking algorithms. Our experienced clinicians and engineers collaborate to provide a quick and accurate solution to any clinical need, using advanced AI technology. Contact us today to add this capability to your portfolio!

 Urology
Urology