According to the CDC, over 41,000 men and 24,000 women are diagnosed with renal cancer in the US each year, and about one fourth of those diagnosed die from the disease. While a wide variety of renal cancer types exists, renal cell carcinoma (RCC) covers about 90% of renal cases. RCC includes several different subtypes: clear cell renal cell cancer (ccRCC) – the most common subtype of RCC, non-clear renal cell cancer – a rarer type which includes papillary RCC (pRCC), chromophobe RCC and other unclassified types. Other types of cancers include transitional cell carcinoma (TCC), Wilms tumor (nephroblastoma) and renal sarcoma. This article focuses on the many ways artificial intelligence (AI) is driving forward the field of renal cancer diagnosis and treatment by introducing breakthrough innovations; in particular, robotic surgery for renal cancer.
Classification for Renal Cancer
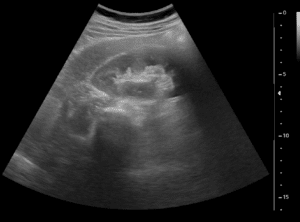
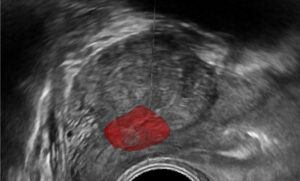
Due to the multitude of renal cancer types, and since each type of cancer may demand a different course of treatment, accurate classification of the cancer type is an imperative factor in the diagnosis process. However, imaging small renal masses (SRMs) is no easy task: differentiating between benign and malignant SRMs and determining the type of malignant tumor are difficult tasks in image processing. State of the art classification networks that are trained on SRM-data provide good results, which are improved by combining auxiliary segmentation loss. Classification is found to work well on CT and MDCT images, as well as spectroscopy images. Two types of classifications are performed – Classification of SRMs into benign (AML – angiomyolipoma) and malignant (RCCs), and Classification of malignant SRMs into different types of RCCs and different tumor grades.
RSIP Vision’s vast experience in AI and computer vision can assist in classifying SRMs resulting in improved diagnostic accuracy and enhanced personalized treatment for patients.
Robotic assistance in nephrectomy
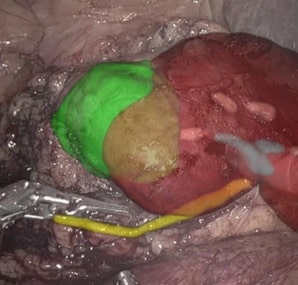
In recent years, robotic assistance in surgeries has gained increased traction in both complete and partial nephrectomies. In these cases, surgical planning and 3D reconstruction based on CT and MRI images play vital roles in a successful robotic-assisted procedure.
RSIP Vision has years of hands-on experience in developing such technologies and solutions, both in surgical planning and 3D reconstruction, which has been shown in prostate cancer surgeries. This expertise, alongside proven capabilities in video analysis and navigation during interventional procedure, helps improve the surgical outcome in nephrectomies.

 Urology
Urology