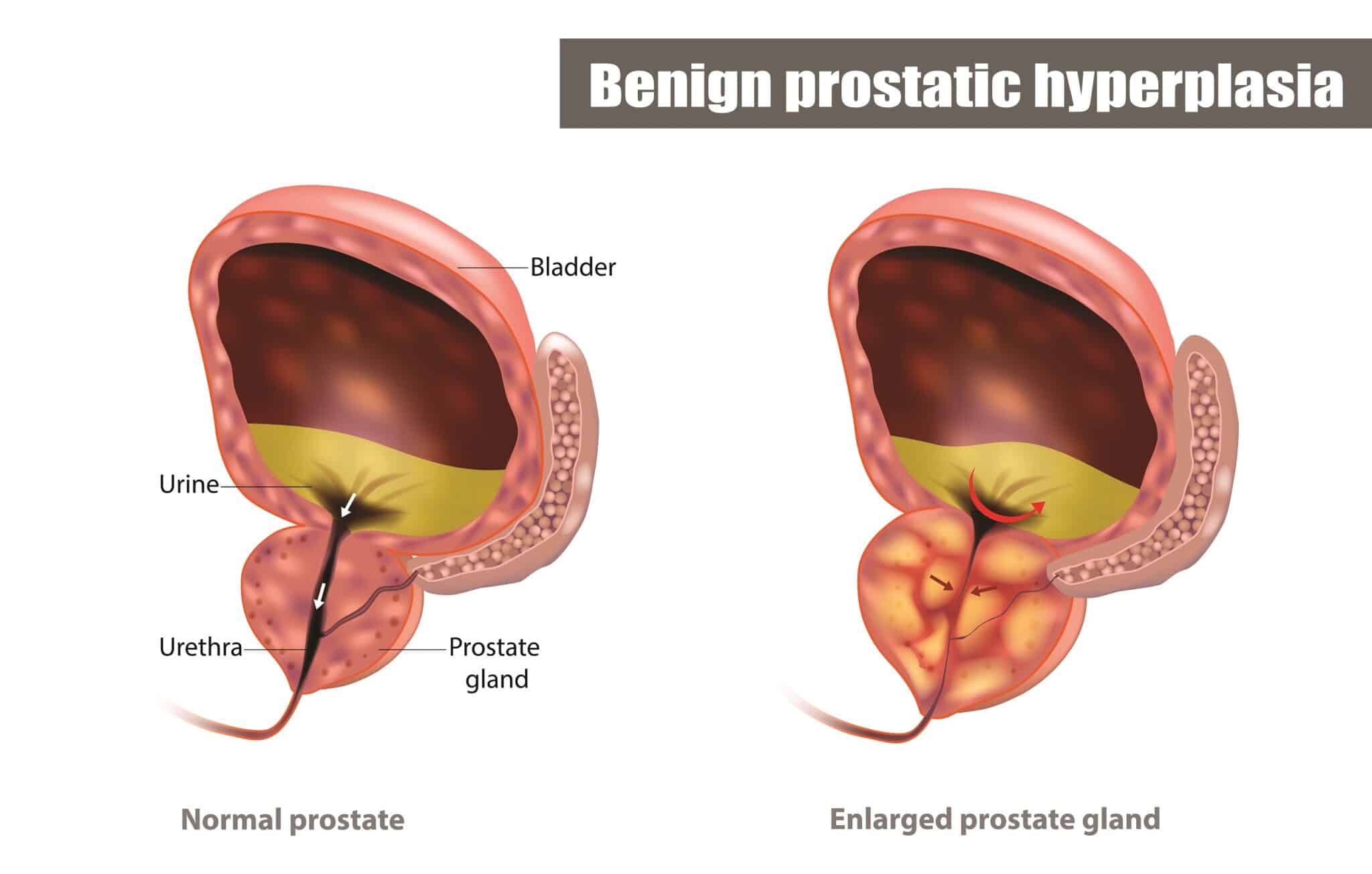
How can Artificial Intelligence benefit urology patients, in particular those affected by prostate BPH (Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia)? AI-based solutions for urology applications are under development and promise important breakthroughs in both operation planning and treatment.
The first type of the BPH treatment is typically non-invasive and based on medications. Some patients subsequently move to intrusive solutions, These are mostly minimally invasive and mainly endoscopic. AI can provide a great contribution to the planning of the surgery: advanced AI algorithms might foresee some complications in advance and provide valuable information to the urologist. During surgery, automatic cystoscopy analysis might show two patients’ prostates that may look similar on camera, but only one of them will bleed during surgery. An AI model that can predict a tendency to bleed will be very helpful in planning the intervention.
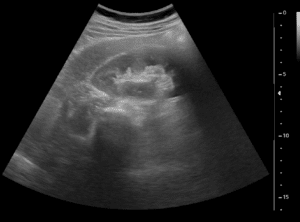
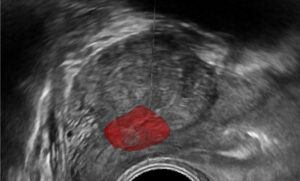
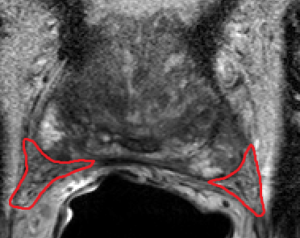
AI can also help the surgical team in that it organizes existing information in a more ordered way: CT and ultrasound scans include much information which is not immediately and fully clear to the surgeon. This includes details about the exact anatomy of the organ, its shape and size.
Invasive treatments of BPH can be of several types: Prostatic Artery Embolization is an invasive radiology treatment, which consists of an arterial catheterization to interrupt the flood of blood to the prostate causing a gradual reduction in size. This intervention is not widely adopted yet but is considered a reasonable option. A similar venous catheterization is currently under research but is not yet approved. AI can analyze angiography and provide precious information such as distance measurements, recommended intervention location, etc.
Another option is placing a mechanical stent in the urethra to expand the regions obstructed by the enlarged prostate. This apparatus needs to be positioned correctly, a task which can be made much easier by using computer-vision-based measurements.
Another method is Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP). By resecting the adenoma (the benign tumor), the urethral blockage is removed, its passage is enlarged and made perfectly operational. Surgeons identify the verumontanum, a structure located on the floor of the posterior urethra which designates the limit of the sphincter, a landmark beyond which the surgery cannot go, to avoid harming the continence of the patient. AI can assist in detecting these regions automatically and accurately.
Other methods for Adenoma removal use various energies. Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) is an endoscopy-based minimally invasive procedure for BPH, by which the adenoma is “peeled off”. This technique is usually indicated for larger prostates than TURP(>80cc),. Since the enucleation is in an a-vasculare plain, bleeding is minimal. AI can make a great contribution to both TURP and HoLEP, in that it suggests the exact plain for the surgeon. Also, the learning curve for a surgeon to perform HoLEP is very steep, and AI might shorten it.
Other energy sources include green light laser, aqua ablation, vapor, etc. The goal of all of them is to clear the obstructing tissue.
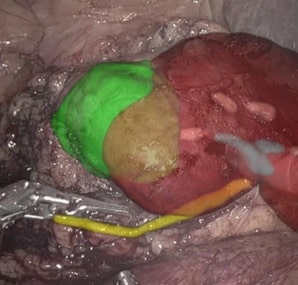
The same can be said for the most invasive BPH procedures like simple prostatectomy (open/robotic). AI can assist in the navigation and detection of various regions, including the critical points which must be considered in the patient’s anatomy. Read more about AI for urology solutions.

 Urology
Urology