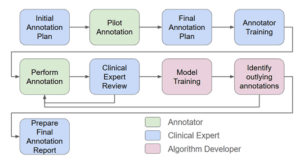
3D models of joints and bones are widely used for a large variety of orthopedic clinical purposes including preoperative planning, patient specific implant design, jig printing, intraoperative navigation and other clinical purposes for which precise and detailed anatomy is required. An example of such a procedure for which a 3D model of joints is required is Arthroplasty. Arthroplasty, one of the most common procedures in the US with more than 1 million procedures performed annually, is an orthopedic surgical procedure that aims to restore functionality and relieve pain by a full or partial replacement or remodeling of joints. This procedure goes through high-complexity steps, starting from planning to execution, all requiring accurate understanding of the patient anatomy, often represented in 3D models.
Arthroplasty outcomes are highly dependent on the technique accuracy, during both planning and operation. Different types of Patient Specific Instrumentation (PSI) were developed for the purpose of elevating accuracy and improving fit of the implant to individual patients’ anatomy. Fine adjustments and precise implant fit during pre-operational planning using technological solutions producing accurate and detailed 3D models of the joints significantly improve procedure outcomes. A multitude of additional new innovative technologies aiming to improve procedures’ outcomes are being developed – starting from automated planning, through robotic surgeries and usage of augmented reality. All of these require precise anatomical 3D information.
The standard 3D reconstruction is based on the 3D information captured in CT scans. Along with the benefit of having the information required for the generation of such models, CT scans have significant operative barriers including low accessibility, high costs and reimbursement difficulties. From the clinical perspective, for gaining high precision 3D information, CT scanners expose patients to high doses of ionizing radiation.
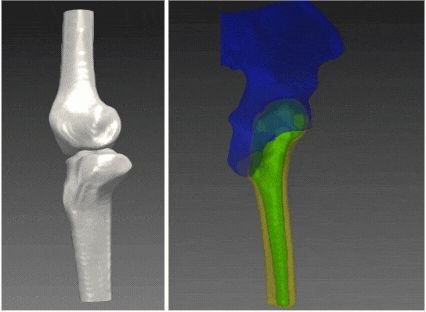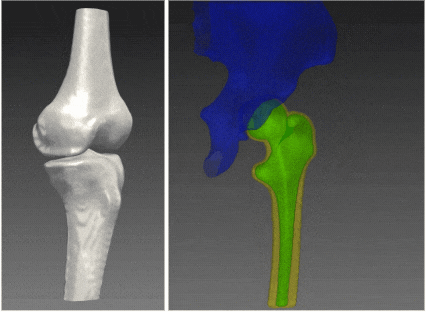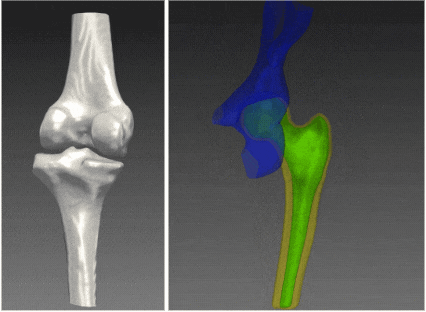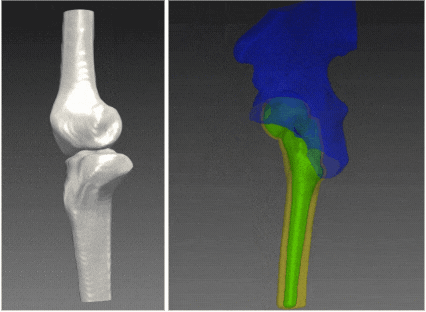
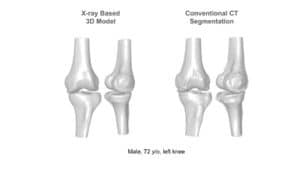
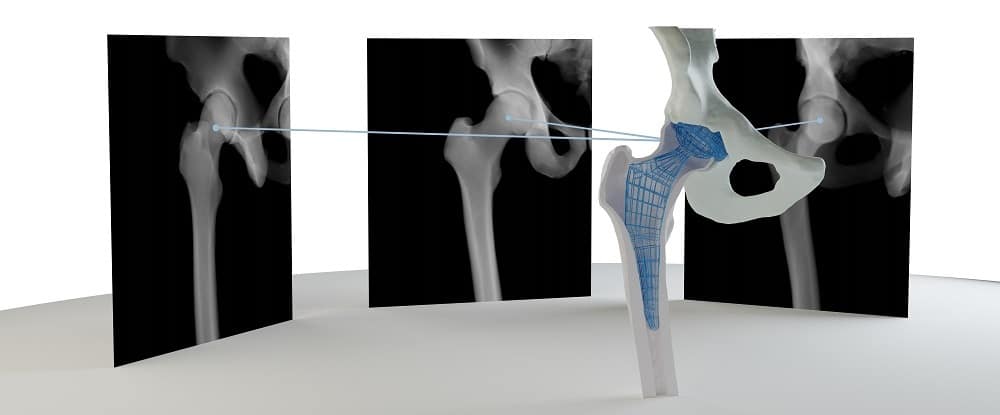
RSIP Vision’s 2D to 3D reconstruction technology enables a clinical-grade 3D reconstruction of the bone from two or more 2D standard X-ray images without the need for CT scan. Using advanced artificial intelligence algorithms and deep-learning based models that allow capturing statistical information and features represented in complex data, this technology enables an end-to-end interpolation of the 2D information into 3D and reconstruction of a highly accurate 3D model. The resulting 3D model provides the information required for the variety of clinical purposes while replacing the need for a full CT scan. The alternative usage of x-ray images allows reduction in radiation, lower-costs with higher reimbursement rates, and higher accessibility, significantly improving the existing pipelines. These benefits potentially influence all parties involved, including patients, clinicians and healthcare providers.
Clinical evaluation of RSIP Vision’s 2D to 3D Reconstruction technology indicates sub-mm accuracy for the knee bones 3D-reconstructed from x-ray images. The technology is now extended for additional joints including hip, ankles and shoulders, and can potentially be extended to any other bony structure.
RSIP Vision is a global leader in artificial intelligence and deep learning for medical imaging with proven industry experience developing clinical-grade breakthrough AI-technologies. We’ll be happy to introduce you to our extensive records and use our experts to find the right solution for boosting up your product.
For more info go to: www.xplan.ai